Burst Testing
This Application Note describes how burst testing is accomplished using a manual regulator and a precision flow control on the Sprint iQ leak tester.
Many devices are constructed with passages that must remain open if the product is to function normally when used. During the manufacturing process, it is sometimes possible to inadvertently create a blockage in a passage thus affecting the quality and performance of the device. It is often necessary to test products to ensure pathways are open and have not become blocked or partially obstructed. This functional evaluation is generally referred to as “occlusion testing.” When checking products for possible blockage, test engineers are frequently concerned with testing speed and repeatability.
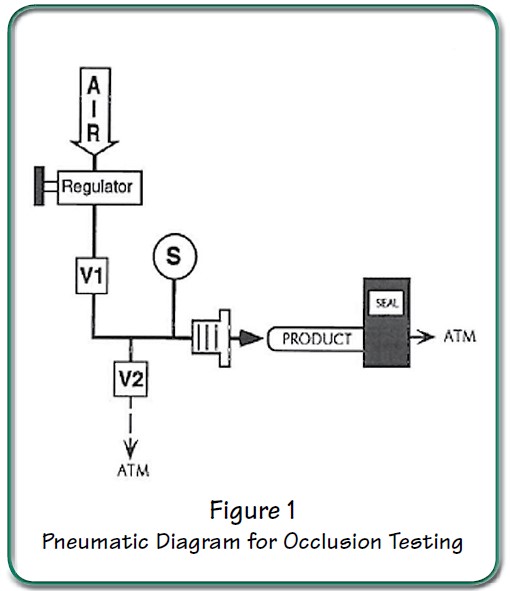
Uson testers can conduct occlusion tests by using a pressure drop technique. In this test, the product must drop below a preset pressure (reject level) to pass the test; the opposite of a normal integrity test. The same basic pneumatic circuit employed in pressure decay testing is used in occlusion testing. Only the programming is different. Thanks to the commonality of test circuits, it is possible (and quite common) to conduct pressure decay tests followed by occlusion tests. This is easy to accomplish with a Sprint iQ and program linking capability.
Sprint iQ tests for occlusion like this:
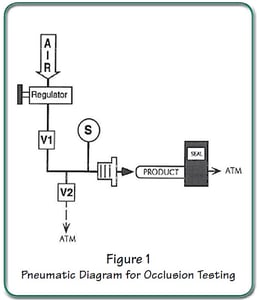
Figure 2 illustrates a typical occlusion test sequence in which the product under test fails the evaluation. The product is pressurized while the clamping fixture seals the open end of the product. At the conclusion of fill time, the fill valve closes and traps air in the test circuit. Sprint iQ sequences to test time, the clamp valve opens to atmosphere, and the tester measures the air pressure that escapes from the product.
In this example, the product fails because the air loss from the product was not great enough to drop below the reject level in the allowed test time.
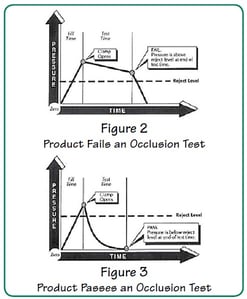
Figure 3 shows a typical occlusion test in which the product passes the evaluation. The product is pressurized while the clamping fixture seals the open end of the product. As shown in Figure 3, the pressure drops below the reject limit within the established test time after the sealing clamp opens and allows the product to flow to atmosphere.
The significant pressure drop in the product indicates that the device under test flow freely to atmosphere and thus is not blocked.
Sprint iQ occlusion testers can be used to test tubes, valves, and devices that must flow a minimum volume of air.
Consider using an occlusion test in conjunction with an integrity test. Depending on the product, multiple occlusion tests can be conducted either sequentially or concurrently. Call Uson to learn how an occlusion test can be used with your particular application.
This Application Note describes how burst testing is accomplished using a manual regulator and a precision flow control on the Sprint iQ leak tester.
Uson offers equipment and solutions for effective catheter leak testing using our Sprint mD multi-function leak and flow tester.
Using Autocouple devices when leak testing smooth tubes and rough or irregular surfaces allows for maintaining a leak-tight seal.
Industries